
Introduction
CRM software is very helpful for businesses that want to improve customer relationships, optimise operations, and increase profits. CRMS allows companies to control customer interactions, automate sales, and learn about their customers' habits. However, using and interacting with CRM software have some issues of their own.
Organisations generally face problems like low data quality, low user adoption, integration problems & lack of customisation. These cause delays, wasted money, and frustration for employees. Occasionally organisations spend a great deal of money on CRM software but it is not effective because it was set up or used incorrectly.
To maximise the use of CRM software, you should address these problems in advance. In this article, we will examine the top 7 problems with CRM that business owners, sales organisations, and CRM managers face. Most importantly, we will provide practical solutions on how to address them so that your CRM software can serve your business objectives.
By the end of this guide, you will know how to optimise your CRM to enhance customer interaction, and business operations, and obtain improved business outcomes.
Struggling with your CRM software? Many businesses invest heavily in CRM but face issues like poor data quality, low adoption, and integration challenges. In this guide, we’ll uncover the top 7 CRM problems and practical solutions to ensure your CRM drives real business success.
1. Data Quality and Duplication
The Challenge
One of the largest challenges in CRM management is data quality. Low-quality data can cause reporting inaccuracies, marketing campaigns to fail, and sales opportunities to be lost. Duplicate or incomplete records or old records can lead to confusion and hinder decision-making by sales and marketing teams. In a research study by Gartner, low data quality costs organisations an average of $12.9 million annually.
Duplicate records are especially troublesome since they can lead to multiple workers contacting the same customer, creating frustration and undermining the credibility of your company. Bad data quality or missing data can lead to miscommunication, follow-up breakdown, and failed sales processes.
The Solution
You can maintain good data quality through a planned approach to data management. Some of the practices include:
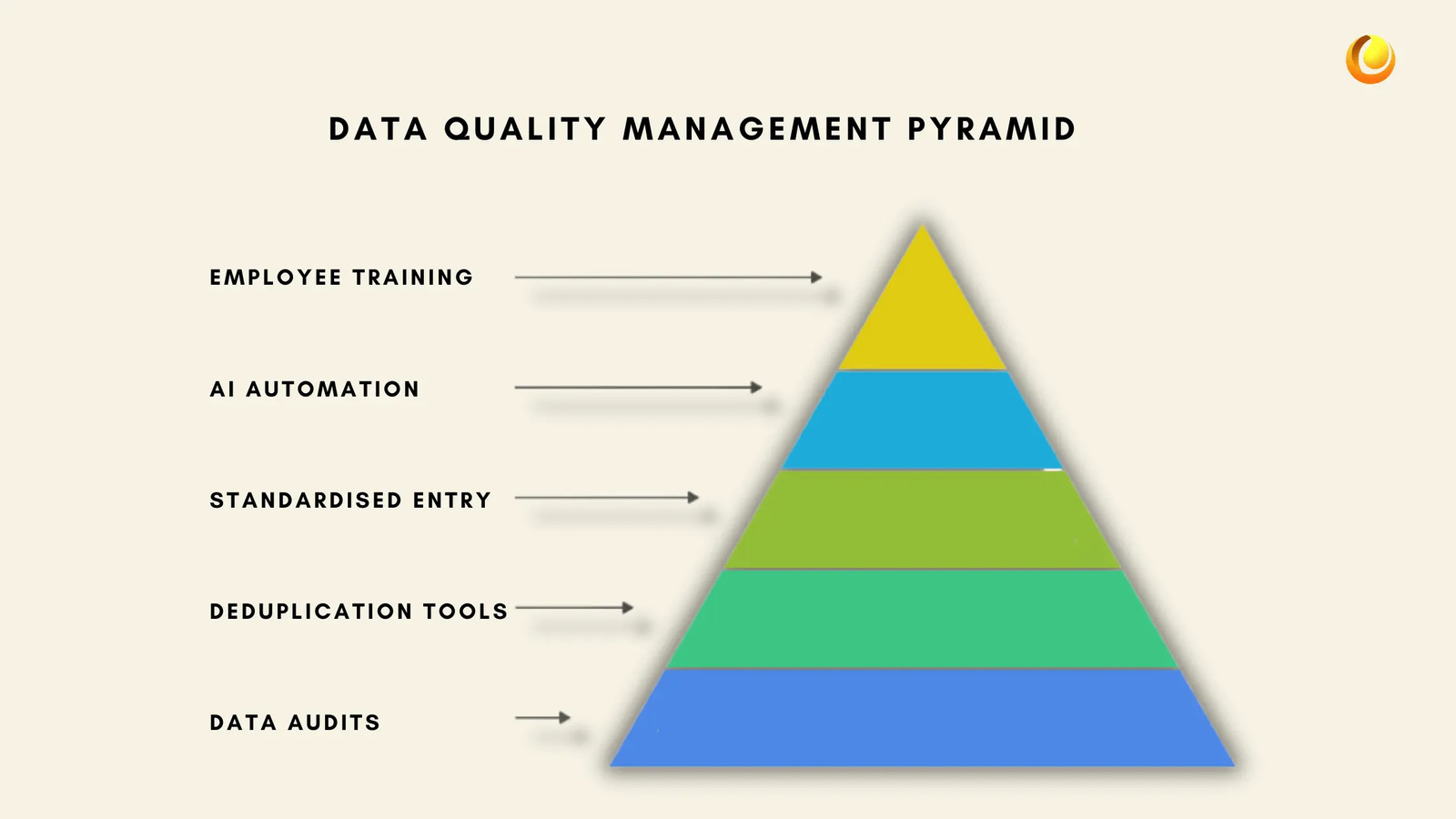
Regular Data Audits: Regular data audits will alert errors and fix them, so your CRM database is fresh and accurate.
Using Deduplication Tools: A majority of modern CRMs like Zoho CRM and Salesforce include deduplication tools that have been coded to combine duplicate records.
Implement Standardised Data Entry Procedures: Make all the staff members enter data uniformly. This includes following the same abbreviations, capitalisation, and naming conventions.
Leveraging AI and Automation: AI-based applications can identify anomalies and recommend fixes in real-time, minimising human mistakes.
Employee Training on Data Hygiene: Employees need to be trained on the need for correct data entry and provided with instructions on keeping clean records.
By focusing on data quality, companies can ensure that their CRM software gives them useful and trustworthy insights, resulting in improved customer relationship management.
2. Low User Adoption and Employee Resistance

The Challenge
One of the most prevalent causes of CRM failure is low user adoption. Employees, especially sales personnel, tend to resist the adoption of CRM software as they see it as unnecessary or time-wasting. Employees in some organisations may find standard approaches such as utilising spreadsheets or putting notes down on their hands easier and believe CRM software adds sophistication to their routine.
This resistance is typically due to a lack of understanding of how CRM software can directly impact them. Without good onboarding and training, employees will find the system daunting and not use it regularly. Therefore, companies fail to reap the full benefit of their CRM investment due to good CRM strategy.
The Solution
To improve user adoption and minimise resistance, companies should strategically approach CRM implementation:
Clearly articulate the advantages: Workers must see how the CRM software will assist them in closing more deals, work smarter, and minimise drudgery. Showing tangible benefits can drive adoption levels.
Apply Gamification Strategies: Engaging leaderboards, rewards, and incentives can make utilising the CRM software more interesting and rewarding. For instance, sales representatives can receive points for logging activity, updating customer information, or closing a deal.
Personalise Dashboards and Workflows: Adapting the CRM experience to fit employee workflows can simplify and make it more intuitive to use. This reduces frustration and enables frequent use.
Provide Hands-On Training and Assistance: Hands-on training, tutorials, and on-demand assistance can enable employees to utilise the system with more confidence. Continuous learning opportunities ensure that users stay up to date with new features and best practices.
Appoint CRM Champions: Designating team members as CRM advocates can help drive adoption by providing peer support and demonstrating best practices.
By fostering a culture of CRM adoption, you can ensure that their teams fully leverage the system’s capabilities, leading to improved productivity and customer management.
3. Integration Challenges with Other Tools
The Challenge
Many businesses rely on multiple software solutions for different operations, such as accounting, marketing automation, customer support, and e-commerce platforms. However, integrating CRM software with these existing tools can be challenging, especially when dealing with legacy systems or software that lacks API support.
Poor integration can lead to:
Data silos where critical customer information is stored in separate systems, making it difficult to get a unified view of customers.
Manual data entry increases the risk of errors and wasting valuable time.
Disruptions in workflow, where sales and customer support teams struggle to access essential customer information.
Without seamless integration, businesses may not be able to fully leverage their CRM software’s capabilities, leading to inefficiencies and missed opportunities.
The Solution
To overcome integration challenges, businesses should adopt the following best practices:
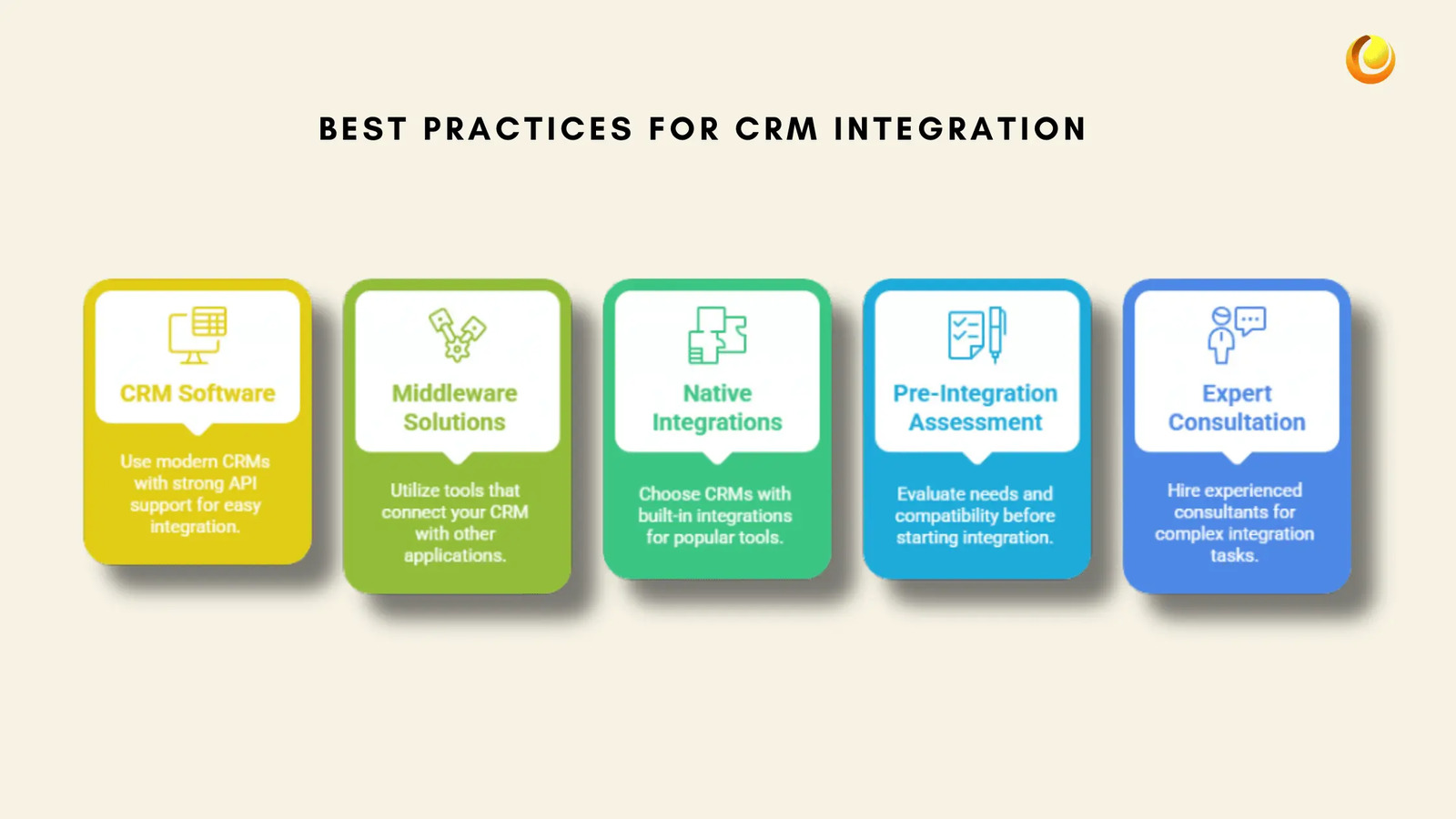
Use CRM software with Strong API Support: Modern CRMs such as Zoho CRM, Salesforce, and HubSpot offer robust APIs that facilitate easy integration with third-party applications.
Leverage Middleware Solutions: Tools like Zapier, and Workato can act as connectors between your CRM and other software, enabling automation without complex coding.
Prioritise Native Integrations: Many CRMs offer built-in integrations with popular tools like Slackand Quickbooks. Opting for native integrations can simplify the process.
Conduct a Pre-Integration Assessment: Before integrating, evaluate business needs, identify critical data points, and ensure compatibility between the CRM and other software.
Hire CRM and Integration Experts: If integration becomes too complex, working with experienced CRM consultants can ensure a smooth and efficient implementation.
A well-integrated CRM software can provide a unified view of customers, streamline operations, and improve team collaboration, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and business efficiency.
4. Lack of Customisation for Business Needs
The Challenge
Every business has unique processes, workflows, and objectives. However, many CRM software come with pre-configured settings that may not align with specific business needs. A CRM that lacks customisation can lead to inefficiencies, forcing teams to adapt their processes to the software rather than the other way around.
Common issues caused by limited customisation include:
Unnecessary fields and features cluttered the interface, making navigating the CRM difficult.
Workflows that do not match the company’s sales and customer service processes.
Lack of industry-specific modules or automation capabilities.
If M software is not tailored to a company’s needs, user adoption may decline, and businesses may fail to see the full benefits of their investment.
The Solution
To ensure your CRM software aligns with your business processes, consider the following customisation strategies:
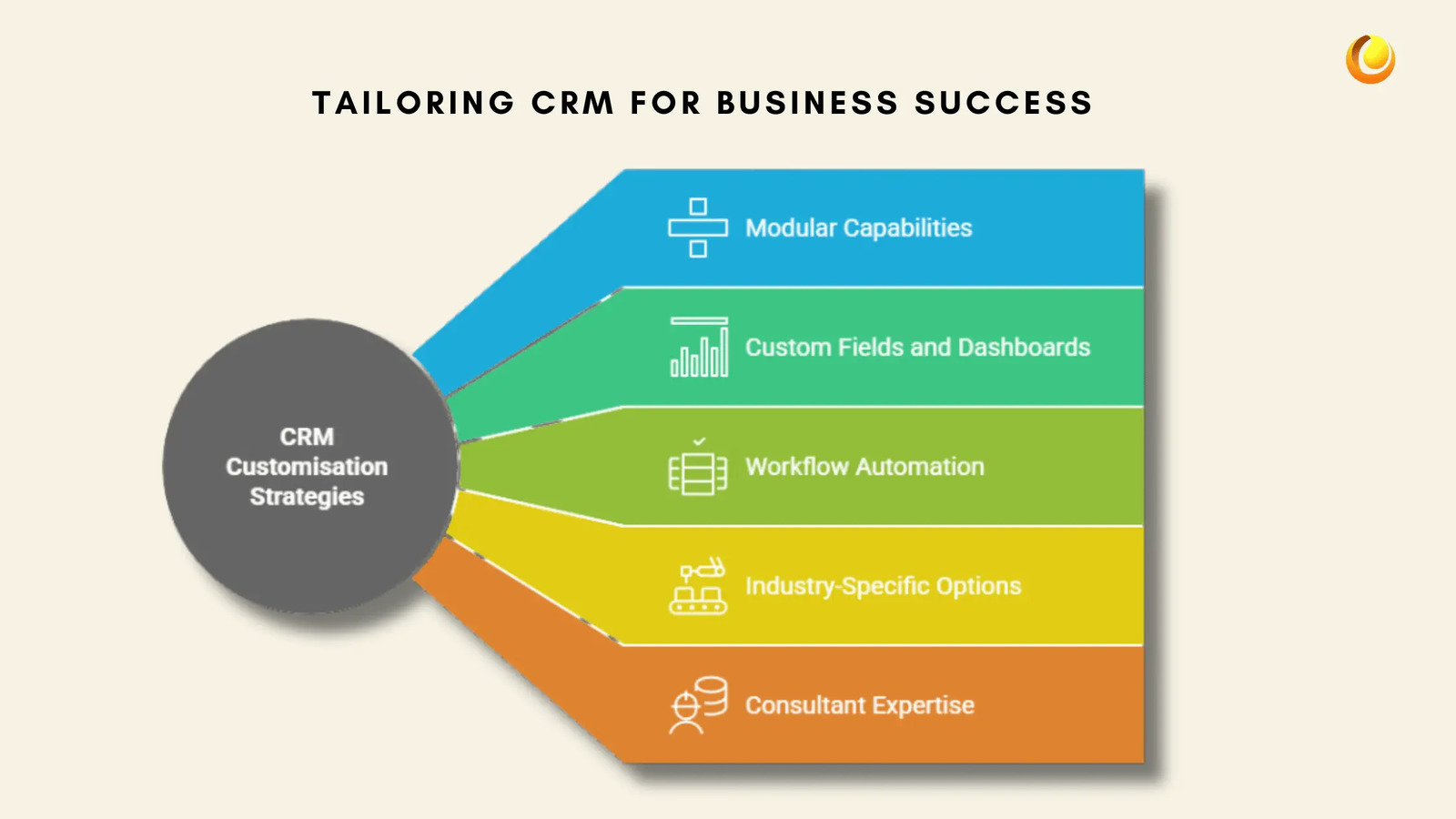
Choose a CRM with Modular Capabilities: Opt for CRMs that allow businesses to enable or disable features based on their requirements.
Customise Fields, Pipelines, and Dashboards: Remove irrelevant fields and create personalised dashboards that display the most relevant information.
Automate Workflows:Set up automation workflows that match your sales and support processes, such as automatic follow-ups, lead scoring, and approval processes.
Utilise Industry-Specific Customisation Options: Some CRMs offer industry-focused templates and modules, which can be a great starting point for tailored configurations.
Work with a CRM Consultant: If in-house expertise is limited, hiring a CRM consultant can help configure the system for optimal performance.
By customising your CRM software effectively, you can improve efficiency, reduce frustration, and ensure that the system enhances rather than hinders your business operations.
5. Inadequate Training and Support
The Challenge
Even the most feature-rich CRM will fail if employees are not properly trained to use it. Inadequate training can lead to underutilisation of key features, data entry errors, and resistance to change.
Additionally, businesses may struggle with limited vendor support, especially when using free or lower-tier CRM plans. This can make it difficult to resolve issues quickly, leading to delays and disruptions.
The Solution
Providing comprehensive training and ongoing support is essential for CRM success. Here’s how businesses can address this challenge:
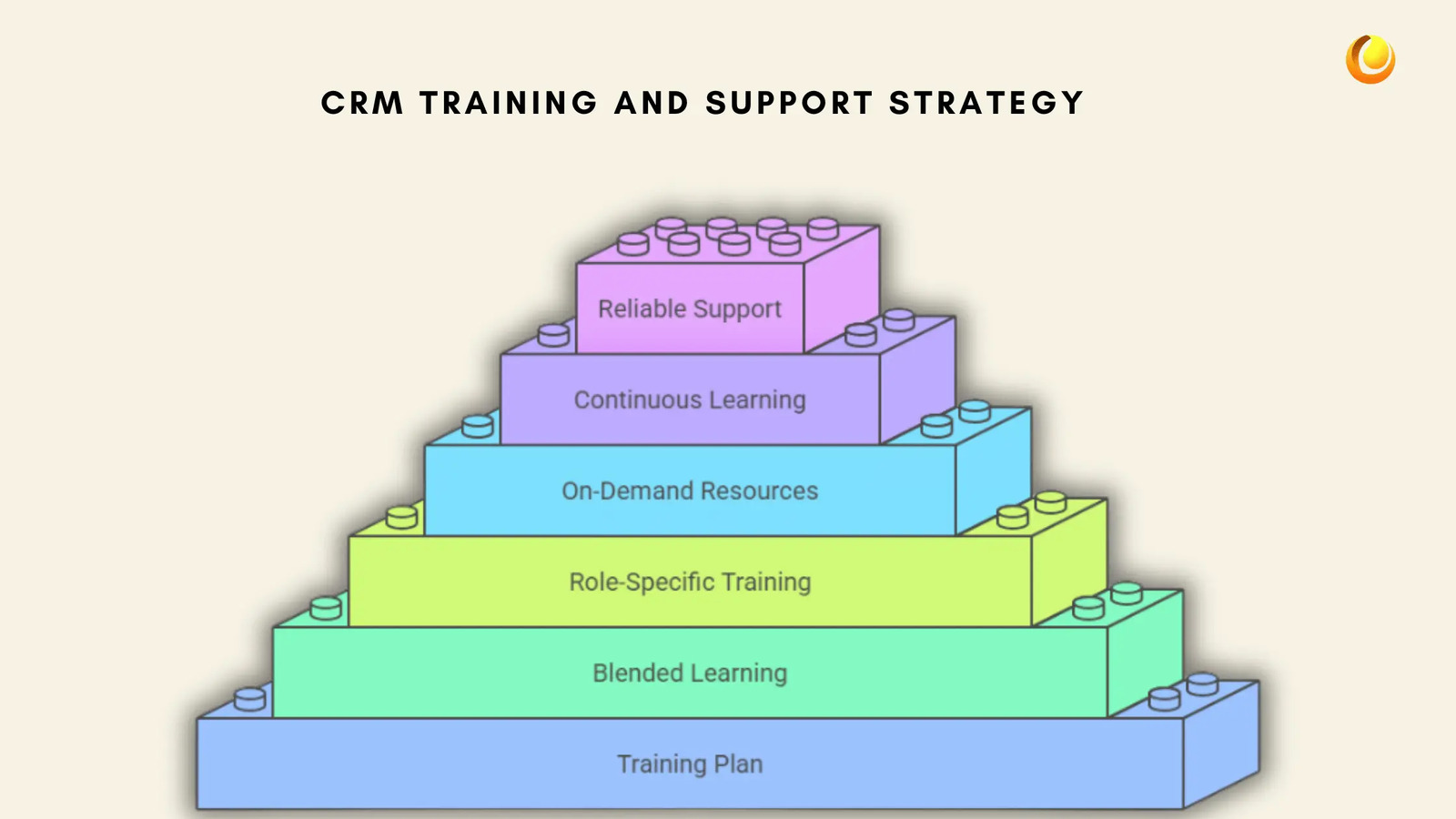
Develop a Training Plan: Offer structured training sessions covering CRM basics, data entry best practices, and advanced features.
Use a Blended Learning Approach: Combine in-person workshops, video tutorials, and interactive guides to cater to different learning preferences.
Offer Role-Specific Training: Sales, marketing, and customer support teams use CRMs differently, so tailor training to their specific needs.
Provide On-Demand Resources: Maintain a knowledge base with FAQs, step-by-step guides, and troubleshooting tips.
Ensure Continuous Learning: CRM software evolves, so offer refresher courses and update employees on new features.
Choose a CRM with Reliable Support: Consider CRM vendors that provide 24/7 customer support, live chat, and dedicated account managers.
Well-trained employees are more confident in using the CRM, leading to higher efficiency, better data quality, and improved customer engagement.
6. Poor CRM Software Reporting and Analytics

The Challenge
CRM software is only as valuable as the insights it provides. Many businesses struggle with generating meaningful reports and analytics due to:
Lack of standardised data entry – Inconsistent data formatting makes it difficult to generate accurate reports.
Overcomplicated dashboards – If reports are too complex, teams may not use them effectively.
Limited custom reporting options – Some CRMs only offer basic reports that do not align with business needs.
Failure to track key performance indicators (KPIs) – Without proper tracking, businesses miss out on opportunities to optimise sales and customer service efforts.
Poor CRM software reporting leads to missed insights, ineffective decision-making, and an inability to measure performance accurately.
The Solution
To improve CRM reporting and analytics, businesses should:
Define Clear Metrics and KPIs – Identify the most relevant performance indicators for sales, customer service, and marketing (e.g., lead conversion rates, sales cycle length, customer retention rates).
Customise CRM Dashboards – Tailor dashboards to display key insights at a glance, making data more accessible for teams.
Automate Reports – Set up scheduled reports to be generated and emailed automatically to stakeholders.
Train Teams on Data Entry Best Practices – Ensure data consistency to improve the accuracy of reports.
Integrate CRM with Business Intelligence Tools – Use tools like Zoho Analytics, Tableau, or Power BI for deeper insights and advanced visualisation.
With accurate and actionable CRM software reports, businesses can make data-driven decisions, improve forecasting, and enhance customer relationship strategies.
7. Security and Data Privacy Concerns
The Challenge
CRM software stores vast amounts of sensitive customer data, including contact details, transaction history, and communication logs. Without robust security measures, businesses are vulnerable to:
Data breaches and cyberattacks – Hackers target CRMs to steal valuable customer information.
Unauthorised access – Employees with excessive permissions may access and misuse confidential data.
Compliance issues – Businesses must adhere to regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and other data protection laws.
Data loss – Accidental deletions, system failures, or lack of backups can lead to critical data loss.
Failing to address security risks in CRM software can result in financial losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences.
The Solution
To ensure CRM security and data privacy, businesses should:
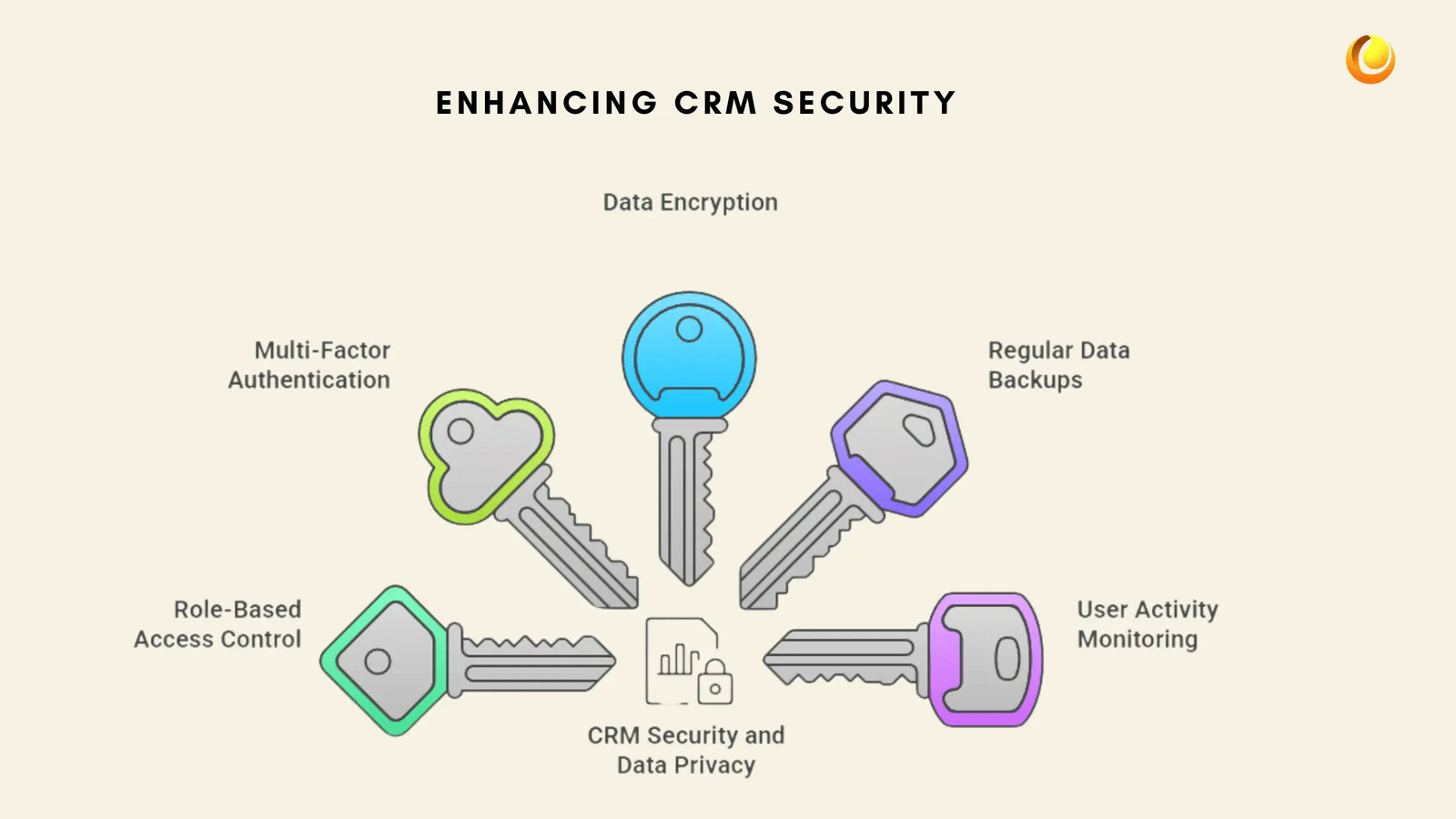
Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) – Restrict access based on user roles to prevent unauthorised data exposure.
Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – Add an extra layer of security to prevent unauthorised logins.
Encrypt Data – Ensure data is encrypted both in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorised access.
Regularly Backup Data – Automate backups to secure cloud storage or external servers to prevent data loss.
Monitor User Activity – Track login history and data modifications to detect suspicious activities.
Ensure Compliance with Regulations – Regularly review CRM security settings to align with industry regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Choose a CRM with Strong Security Features – Opt for CRM software that offers advanced security protocols, such as Zoho CRM, Salesforce, or HubSpot.
By prioritising CRM security, businesses can protect sensitive data, maintain customer trust, and avoid regulatory penalties. Use the best CRM strategies to get ahead in the competition.
Conclusion
A well-implemented CRM software can transform how businesses manage customer relationships, improve sales performance, and enhance overall efficiency. However, common CRM issues such as data duplication, low user adoption, integration challenges, and inadequate training can hinder success.
By proactively addressing these challenges with strategies like regular data audits, gamification for user adoption, API-based integrations, workflow customisation, and continuous training, businesses can fully optimise their CRM software.
Now is the time to evaluate your CRM setup and identify areas for improvement. Start by conducting a CRM audit, engaging employees in training sessions, and implementing automation to streamline processes.
Need help optimising your CRM? Work with our experts and transform your business.





